How often does your house burn down? Pretty frequently it appears if you are a Google exec. As I’m sure most of you are aware Google have just bought Nest, the “unloved home products” manufacturer (not the “unloved, home products manufacturer”) known for their thermostats and smoke detectors.
To excuse the pun but is this a case of Google having money to burn or a pointer towards something more significant for the emerging IoT industry? In my opinion it’s probably a bit of both. First of all current Nest products are niche and will only appeal to gadget freaks or maybe people with OCD who need to regularly check if their house is on fire. A $150 price point for a smoke alarm when I can get one for less than $10 will strangle adoption.
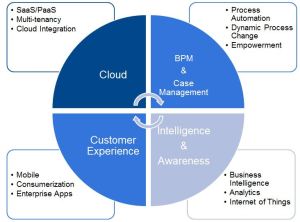
In a previous post I stated that all of the data generated by IoT devices is only of use if it is connected to business processes. Successful IoT companies will produce solutions for essential business or consumer problems not just smart devices.
It has been said elsewhere that there are two IoTs, one for industry and one for consumers. The industrial IoT is alive and well providing things like monitoring and control of for example essential and dangerous business processes. When it comes to consumer IoT successful products will be those that also trigger essential but mundane processes and services for the end user (e.g. car repairs and essential home maintenance) or provide important personal and environment monitoring services (e.g. health, weather and traffic monitoring). Getting back to Nest it’s not the thermostat that needs web enabled it’s the boiler/furnace. Being able remotely adjust my thermostat is not an essential service however I’d really like a call out to be automatically triggered if my boiler/furnace breaks down. Knowing my house is one or two degrees warmer than it should be isn’t critical. I need to know quickly if an elderly relative has remembered to take prescribed medicine or had an accident in their home. $200 fridges, kettles or toasters are non-essential items and don’t need internet connectivity. The core objective of a domestic smoke alarm is to get people out of a house before a fire takes hold, it doesn’t need to be web enabled.
Nest CEO Tony Fadell told WIRED “Both companies believe in letting the technology do the hard work behind the scenes so that people can get on with their lives,” This statement I think implies an understanding of the key role business process automation will have on the successful adoption of IoT. At the moment Nest products provide the Internet of Things for devices that don’t need to be connected to the internet. However I think Google are buying the technology, patents and potential roadmap rather than the current product suite?
Successful IoT companies won’t simply supply devices, they’ll provide business and customer process solutions.